Joint pain can be discomfort, pain, and inflammation from any part of the joint like the tendons, muscles, bone, ligaments, and the cartilage.
In majority of the cases, joint pain is also the term given to arthralgia or arthritis.
Arthritis is characterized by inflammation or pain within the joint itself.
However, joint pain can also be attributed to several other conditions like gout, bursitis, osteoarthritis, sprains, strains, rheumatoid arthritis, and other injuries.
While it affects any part of the body, pain in the knee is the most common, followed by shoulder and hip pain.
As a person gets older, joint pain has the tendency to occur more often.
Joint pain can range from irritating to debilitating.
Acute cases will disappear after a few weeks while chronic cases can persist for several weeks or even months.
Unfortunately, however the short term the pain and swelling can be, it can still affect the patient’s life quality.
For those who are suffering from pain in the joint, some of the common treatment options can include:
Medications
For moderate to severe joint pain, prescription or OTC nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) are often recommended for pain relief.
Patients who experience only mild pain san swelling, acetaminophen (Tylenol) will be prescribed.
For joint pains that are severe, a strong opioid medication may be prescribed by the doctor.
Other medication that might be given to help ease the pain can include:
- Muscle Relaxants – given to combat muscle spasms. Muscle relaxants are often used with NSAIDs for more potent results.
- Antidepressants and antiepileptic drugs – both interfere with pain signals.
Topical Agents
A substance found in chili peppers known as capsaicin has been known effective in relieving joint pains.
It works by blocking substance P, the substance known to help transmit pain signals.
It also triggers the release of body chemicals that help block the pain.
These chemicals are known as endorphins.
Ben Gay and other topical creams that contain methyl salicylate are also known to provide relief for joint pains.
Injections
When topical and oral medications won’t work, steroid medications might be the next treatment option recommended.
A steroid medication is injected into the joint every 3 to 4 months to help ease the pain.
This treatment route is often recommended for patients with joint disease, tendinitis, and arthritis.
Physical therapy
Physical therapists help patients with joint pain by strengthening the muscles around it, improving the motion range of the patient, and stabilizing the joint.
Techniques like ultrasound, heat and cold therapy, and electrical nerve stimulation may also be used.
For overweight patients, getting rid of the extra pounds might be recommended in order to take pressure off the painful joint.
While exercise is a good and effective way of losing the extra weight, not all exercises will do.
As a general rule of thumb, it is recommended that you stick to low-impact exercises like swimming and bicycling.
Doing low impact exercises is recommended so joint irritation is avoided.
Home Remedies
To relieve short term pain at home, the following are recommended:
- Protecting the joint with the use of a brace or wrap
- Resting the joint and avoiding activities that might cause pain
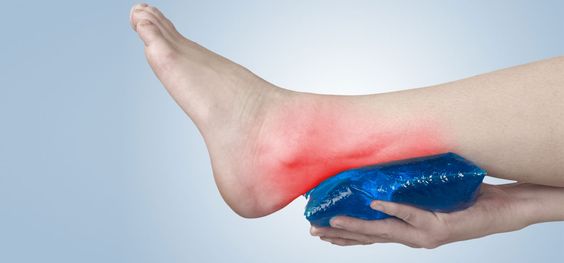
- Putting ice on the painful joint for at least 15 minutes, several times daily
- Compressing the joint using an elastic wrap
Applying ice to the joints that are painful have also been proven to relieve both the inflammation and the pain.
Using a heating pad or a wrap several time a day is also considered an effective way to combat muscle spasms around the painful joint.
If joint pain is keeping you from doing your day-to-day activities, please visit www.bjios.sg for help.