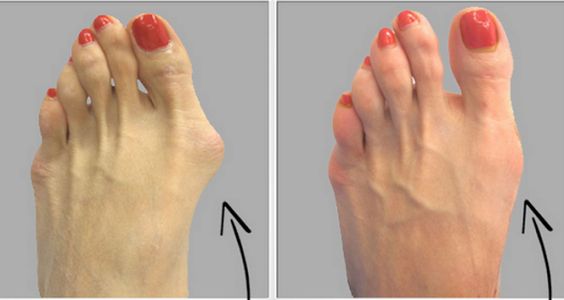
A bunion is characterized by an unnatural and bony hump that develops in the big toe’s base.
It is also sometimes referred to as hallux valgus.
The condition may sometimes result to calluses and can be very painful.
Treatment options for the condition can vary.
It can also range from over-the-counter medications to bunions surgery.
Causes
Some experts believe that narrow, tight, and high-heeled shoes can contribute to the development of bunions.
Other likely causes can include:
- Inherited foot type
- Injuries of the foot
- Congenital deformities
Symptoms
Bunion has several symptoms.
Some of the most common include:
- Soreness, swelling, and redness in the area affected
- Bulging bump on the outside of the base of the big toe
- Thickening of the skin found at the base of the big toe
- Corns or calluses
- Persistent or intermittent pain
- Limited movement of the big toe
Diagnosis
While it’s easy to diagnose bunion based on the unusual shape and the pain, in some instances, other tests might be needed.
For example, the doctor might recommend an X-ray to assess the extent of the deformity.
Blood tests might also be necessary to check if the pain can be the result of a certain kind of arthritis.
Depending on the evaluation, the doctor will decide if orthopedic shoes, medications, custom made inserts, or bunions surgery might be the right treatment option.
While majority of the cases will not require medical treatment, seeking medical attention might become necessary if the following symptoms are present:
- Persistent big toe or foot pain
- Bump on the joint of the big toe
- Limited movement of the big toe or foot
Risk Factors
Some of the most common risk factors for bunion include:
- High heels – wearing footwear with high heels can force the toes into the front, crowding them in the process
- Arthritis – pain secondary to arthritis can affect the way an individual walks and can make them more prone to developing the condition
- Heredity – individuals with structural foot defects that are inherited may be more susceptible to developing the condition
Treatment Options
To reduce swelling and inflammation, over-the-counter pain relievers might be prescribed.
In some instances, a heating pad or a warm foot bath might also offer the much needed relief from the pain and discomfort.
If pain is not consistent and the condition is in its early stage, using the right footwear might be able to help.
Doctors may also suggest using bunion pads, shoe inserts, and splints as long as it will not put pressure someplace else or cause other foot issues.
Surgery for bunions or bunionectomy can also become the likely treatment option for several cases.
Generally, procedure will involve removal or realignment of the soft tissue and the bone.
The primary goals are relieving pain and restoring normal alignment.
Small wires, plates, and screws may be utilized to help hold the bone in place.
In most instances, regional anesthetic is used during the procedure.
Sedatives may also be used.
Typically, the surgery can last an hour or more.
Bunion Surgery Types
There are more than 100 types of bunion surgeries.
However, no type is considered best as surgeries would need to be specific to the condition being treated.
Some of the most common types of bunions surgery are:
- Exostectomy – this entails removing part of the metatarsal head
- Realigning of the soft tissues (ligaments) located around the joint of the big toe
- Arthrodesis or fusion of the big toe joint
- Osteotomy – involves creation of small cuts in the bones so it can be moved in a normal position
- Implant insertion of artificial joint
For help with bunions, please visit www.bjios.sg.