When cells divide at a rate that is both abnormal and uncontrollable, they form a mass of tissue or lump.
This mass of tissue is often referred to as tumor.
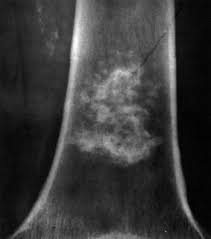
A tumor that forms or develops in the bones is called a bone tumor.
A bone tumor can be malignant or benign.
While the latter is considered non-fatal, it still comes with certain risks and may require treatment.
The former on the other hand is considered life-threatening as there is a possibility for the cancer cells to spread throughout the body.
Likely Causes
While unfortunate to note, no known definite causes have been identified for bone tumors yet.
However, likely causes include radiation, genetics, and bone injuries to name a few.
Osteosarcoma for one has been associated with the use of high doses of anticancer medications as well as high doses of radiation.
Patients with bone fractures repaired using metal implants have also been observed to be more susceptible to osteosarcoma.
Potential Symptoms
Some of the possible indicators of bone tumor include:
Pathologic Fracture
In some cases of undiscovered bone tumors, even a minor injury would be enough to break the weakened bone.
The condition is known as pathologic fracture and it often results to excruciating pain.
In some cases, swelling at the site of the tumor will manifest.
Movement
In some instances, bone tumors that are benign will not manifest any symptoms.
Oftentimes, treatment is not considered necessary.
However, when it starts to interfere with the patient’s function and movement, possible treatment options will be considered.
Dull Ache
One telltale sign of bone cancer is dull ache felt by patients in the affected bone.
In majority of the cases, the dull pain will manifest only occasionally at first.
However, overtime, it can become constant and severe.
In some cases, the pain becomes so severe that it wakes up afflicted patients at night.
Fevers
It is also very likely for people with bone tumor to experience night sweats or fever.
In the absence of night sweats or fever, patients might notice tissue masses on some parts of their body.
Diagnosis

Fractures, infections, and other conditions may sometimes resemble tumors.
That being said, a variety of tests will be required to accurately diagnose the condition.
Some of the tests include:
- Imaging tests
To gauge the size and the tumor’s exact location, an X-ray will be required.
Depending on the results, other imaging tests might also be recommended:
PET scan – can help determine the tumor’s location.
CT scan – can provide a series of highly detailed images that are taken from different angles.
MRI scan – can provide a detailed picture of the area affected.
Angiogram – can provide an X-ray of the blood vessels
- Blood and urine tests
Blood and urine samples will be tested to assess the presence of tumors or other likely medical conditions.
The alkaline phosphatase test is often used to check for bone tumor.
When the tests reveal large quantities of the enzyme in the blood, it can be a sure indicator of bone tumor.
Biopsies are also sometimes recommended in order to get a better insight of the condition.
Either of the two kinds of biopsies might be requested:
- Incisional Biopsy – this kind is also referred to as open biopsy. Unlike needle biopsy, this will require general anesthesia and is carried out in the operating room.
- Needle Biopsy – the procedure is carried out by inserting a needle in the patient’s bone to remove a small part of the tissue. X-ray, MRI or CT scan results will be needed when performing needle biopsy so the location of the tumor can be accurately identified.
While benign bone tumors are common, having it checked by a doctor is still recommended. If you notice classic signs of a bone tumor, it would be best check with the experts at www.bjios.sg.